基于大型语言模型的检索增强生成综述
进阶 RAG 范式与模块化 RAG
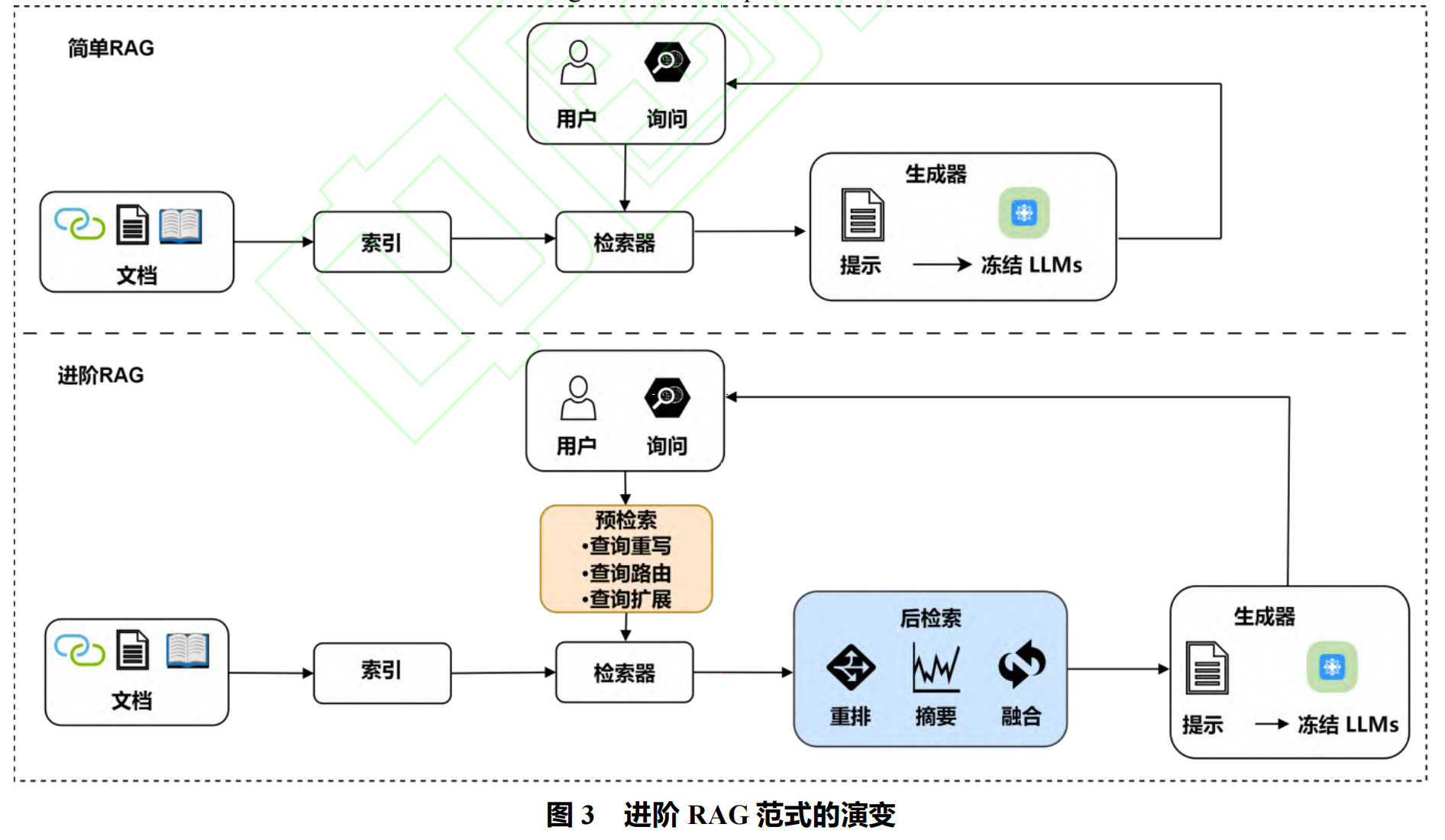
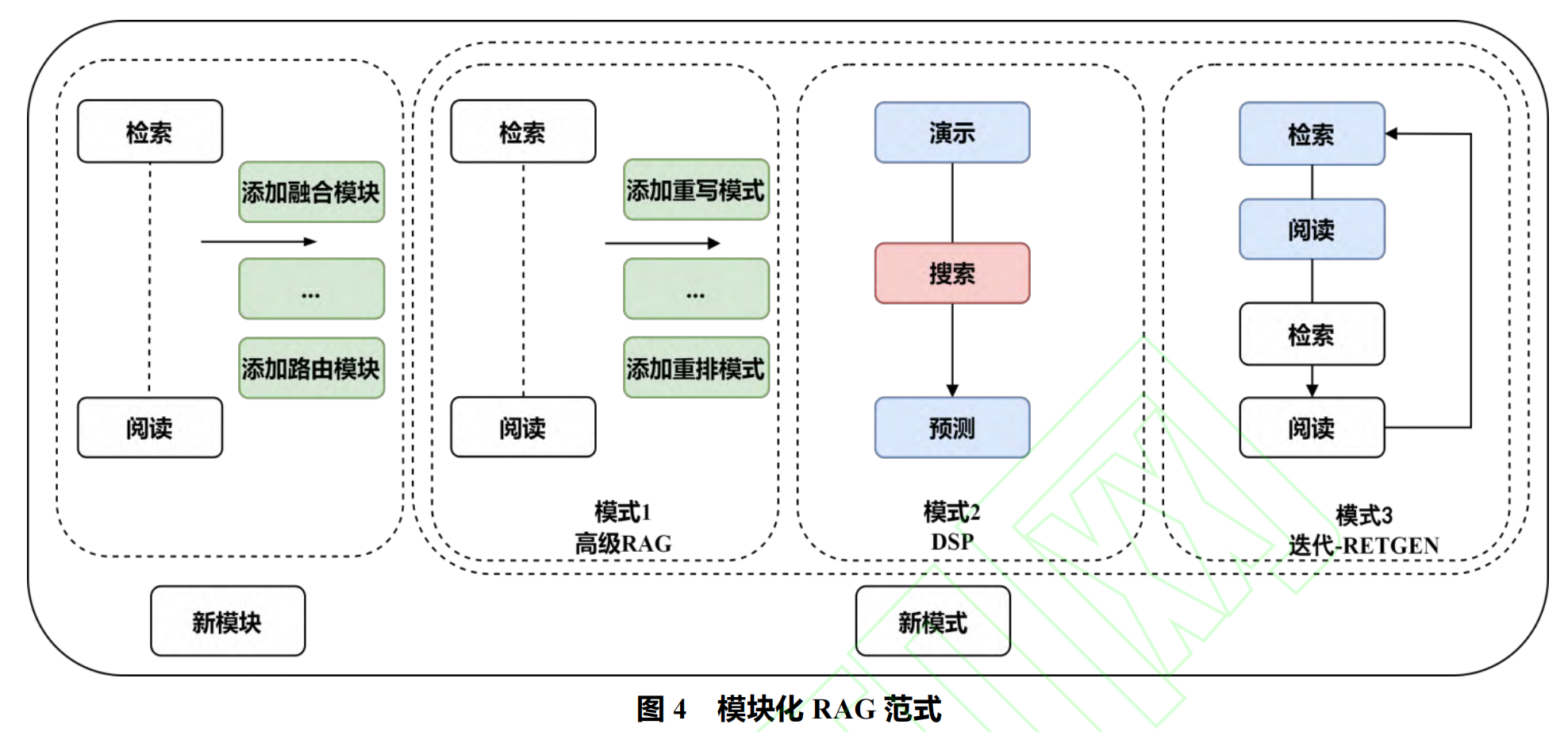
表 1 RAG 方法总结
| RAG 过程 | 文献 | 检索增强生成方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 检索预处理 | SKR[30]、Adaptive-RAG[31] | 基于问题精准的文本解析 |
| 检索预处理 | DenseX[32]、TableGPT[33]、Iseeq[34]、knowledgpt[35]、G-Retriever[36] | 基于外部检索源的文本解析 |
| 检索预处理 | LLAMAi[37]、Small2Big[38]、Meta-Chunking[39]、GLMwCFiCR[40]、RAAT[41] | Chunk 分割(动态分块、元数据增强) |
| 嵌入表示 | C-Pack[46]、RetroMAE-2[47]、REPLUG[48]、Arl2[49]、Promptagator[50]、BGE[51]、AngIE[52]、ListT5[53] | 微调嵌入(领域适配、对齐生成器) |
| 索引 | HyDE[54] | 分层索引(假设文档嵌入优化) |
| 索引 | RAPTOR[55] | 树形索引(分层摘要树) |
| 索引 | KGP[56] | 知识图谱(KG)索引(多文档逻辑关系建模) |
| 查询 | RAG-Fusion[57] | 多响应扩展(并行子查询) |
| 查询 | LTMP-CLR[58] | 子查询(最小到最大提示分解) |
| 查询 | RRR[28]、BEQUE[59] | 查询转换 / 重写(LLM 驱动的长尾查询优化) |
| 查询 | Step-back prompt[26]、FCTG-ICRA[60]、DPR[61] | 查询路由(动态路径选择) |
| 外部适配器 | UP-RISE[62] | 轻量级提示检索器(零样本提示池) |
| 外部适配器 | Search-Adaptor[63]、PRCA[64]、CRAG[65] | 特定任务检索器(插件式适配器) |
| 外部适配器 | GenRead[66]、PKG[67] | 引入 LLMs 生成器(替代传统检索器) |
| 检索信息生成 | RAG-Fusion[57]、Filter-Reranker[68]、G-RAG[69]、RankRAG[70] | 重排(LLM+SLM 协同排序) |
| 检索信息生成 | Lingua[71]、Longllmlingua[72]、FILCO[73]、RECOMP[74]、ACD-RAG[75] | 选择性上下文(噪声过滤与压缩) |
| 检索信息生成 | RAAT[39]、IBP-ENFoRAG[76]、Chatlaw[77] | 信息过滤(LLM 自评相关性) |
| 提示输出 | URR-RAIC[78] | 微调数据(多样化标题增强) |
| 提示输出 | SANTA[79]、DFK-TOD[80]、RA-DIT[81] | 强化学习 / 对齐(KL 散度对齐检索 - 生成偏好) |
| 高级流程优化 | Efficient RAG [85]、Rat [88] 等 | 迭代检索(多轮精炼查询) |
| 高级流程优化 | IRCoT[89]、ToC[90] | 递归检索(链式思维 + 澄清树) |
| 高级流程优化 | Self-RAG[95]、IM-RAG[98] | 自适应增强(反射令牌自主决策) |
表 2 RAG 开源框架
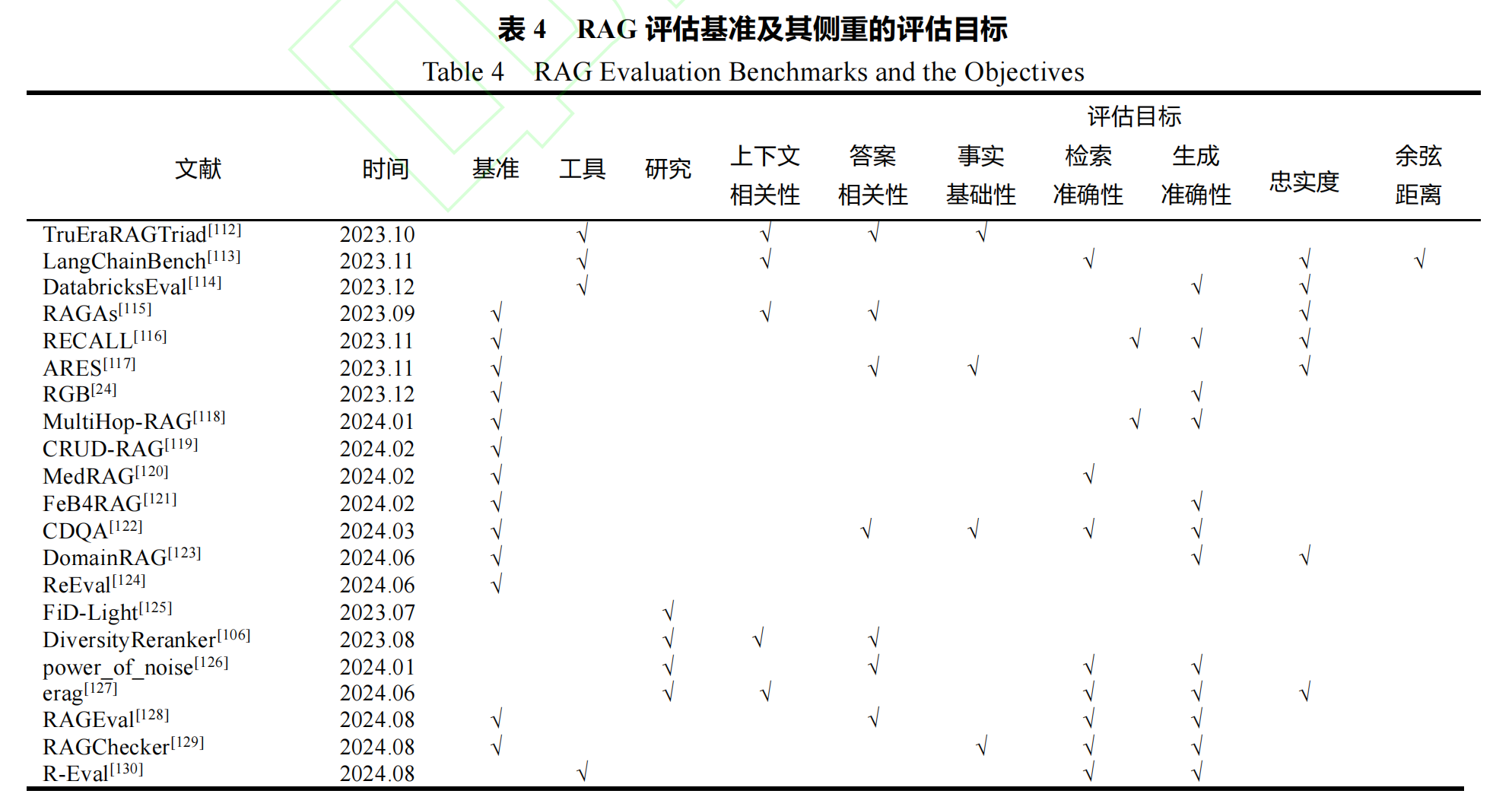
表 3 RAG 评估数据集
| 基准 | 数据集 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| RAGAs[115] | 维基百科 WikiEval | 2022 年后的维基百科页面,测试动态信息处理。 |
| RECALL[116] | EventKG[138]、UJ[139] | 反事实知识鲁棒性评估,含事件图谱与专业术语。 |
| ARES[117] | Hotpot[133]、FEVER[134]、WoW[135]、MultiRC[136]、ReCoRD[137]、NQ[140] | 多任务数据集,覆盖多跳推理、事实验证等。 |
| RGB[24] | 新闻生成数据集 | 在线新闻构建,测试真实世界信息感知。 |
| MultiHop-RAG[118] | 新闻生成数据集 | 多跳问答场景,强调跨文档推理。 |
| CRUD-RAG[119] | 新闻生成数据集、UHGEval [141] | 中文综合基准,含增删改查任务。 |
| MedRAG[120] | MIRAGE | 医疗领域数据集,评估专业知识准确性。 |
| FeB4RAG[121] | FeB4RAG、BEIR[142] | 联邦搜索场景,多源信息检索评估。 |
| CDQA[122] | 新闻生成数据集、Labeller | 动态问答基准,含人工标注真值。 |
| DomainRAG[123] | 高校录取信息生成数据集 | 领域特定动态数据,测试信息更新能力。 |
| ReEval[124] | RealTimeQA[143]、NQ[144] | 实时问答与幻觉检测,含时间敏感数据。 |
| RAGEval[128] | DragonBall 数据集 | 特定领域 “问题 - 参考 - 答案” 三元组,评估有效性。 |
| RAGChecker[129] | 人工注释的偏好数据集 | 细粒度评估,揭示模型行为与人类偏好的对齐性。 |
表 4 RAG 评估指标
| 类别 | 指标 | 定义与公式 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 检索指标 | 准确率(ACC) | Accura**cy=TP+TN+FP+FN**TP+TN | 检索文档与查询的整体匹配度。 |
| 精确率(Prec) | Precision=TP+FP**TP | 检索结果中相关文档的比例。 | |
| 召回率 @K(R@K) | Reca**ll@K=∣R**D∣R**D∩Topkd | 前 K 个结果中相关文档的覆盖率。 | |
| 平均倒数排名(MRR) | MRR=∣Q∣1∑i=1∣Q∣rank**i1 | 首个相关项的排名质量。 | |
| 平均查准率(MAP) | MAP=∣Q∣1∑q=1∣Q∣∣RDq∣∑k=1n(P(k)×re**l(k)) | 所有查询的平均排序精度。 | |
| 精确匹配(EM) | 生成答案与标准答案完全匹配(0/1)。 | 严格事实准确性评估。 | |
| 排名质量(NDCG) | NDCGk=IDCGkDCGk | 文档相关性与排名位置的一致性。 | |
| 生成指标 | ROUGE-N/L | n-gram 重叠度(ROUGE-N)或最长公共子序列(ROUGE-L)。 | 摘要 / 生成文本与参考文本的相似性。 |
| BLEU | BLE**U=BP⋅exp(∑w**nlogP**n) | 机器翻译 / 生成文本的 n-gram 精度。 | |
| BERTScore | 基于 BERT 嵌入的 token 级相似性(P/R/F1)。 | 语义层面的生成质量评估。 | |
| 忠实度(Faithfulness) | 生成内容中可追溯至检索文档的事实比例。 | 避免幻觉,确保知识来源可靠。 | |
| 额外指标 | 延迟(Latency) | 单次查询响应时间。 | 用户体验关键指标,尤其实时场景。 |
| 余弦相似度(CS) | CS=∥A∥∥B∥A⋅B | 检索 / 生成结果的多样性评估(值越低多样性越高)。 | |
| 噪声鲁棒性(NR) | 处理噪声数据时的响应质量保持能力。 | 抗干扰能力,如模糊输入场景。 | |
| 反事实鲁棒性(CFR) | 识别并忽略错误信息的能力。 | 对抗错误检索内容的可靠性。 |
表 5 RAG 评估基准
参考文献
[1] QIAN J, JIN Z, ZHANG Q, et al. A Liver Cancer QuestionAnswering System Based on Next-Generation Intelligence and the Large Model Med-PaLM 2[J]. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology, 2024, 2(1): 28-35. [2] YUE S, CHEN W, WANG S, et al. Disc-lawllm: Fine-tuning large language models for intelligent legal services[J]. arxiv preprint arxiv:2309.11325, 2023. [3] 房晓楠。松鼠 AI 的 “AI+ 智适应教育” 之路该如何走?[J]. 机器人产业,2019 (1): 80-84. FANG X N. How to Walk the Road of “AI+ Intelligent Adaptation Education” for Squirrel AI? [J]. Robot Industry, 2019 (1): 80-84. [4] NIKDAN M, TABESH S, CMCEVIC E, et al. RoSA: Accurate Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning via Robust Adaptation[C]//Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning. [5] LI J, LIU Y, FAN W, et al. Empowering molecule discovery for molecule-caption translation with large language models: A chatgpt perspective[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2024. [6] SHUSTER K, POFF S, CHEN M, et al. Retrieval Augmentation Reduces Hallucination in Conversation[C]// Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2021. 2021: 3784-3803. [7] ZHAO Z, WALLACE E, FENG S, et al. Calibrate before use: Improving few-shot performance of language models[C]//International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2021: 12697-12706. [8] CHENG X, LUO D, CHEN X, et al. Lift yourself up: Retrieval-augmented text generation with self-memory[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2024, 36. [9] GAO L, MADAAN A, ZHOU S, et al. Pal: Program-aided language models[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2023: 10764-10799. [10] HUANG L, YU W, MA W, et al. A survey on hallucination in large language models: Principles, taxonomy, challenges, and open questions[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2023. [11] IZACARD G, LEWIS P, LOMELI M, et al. Atlas: Few-shot learning with retrieval augmented language models[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2023, 24(251): 1-43. [12] WU Y, RABE M N, HUTCHINS D L, et al. Memorizing Transformers[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations. [13] GUU K, LEE K, TUNG Z, et al. Retrieval augmented language model pre-training[C]//International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2020: 3929-3938. [14] LEWIS P, PERES E, PIKTUS A, et al. Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive nlp tasks[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2020, 33: 9459-9474. [15] BORGEAUD S, MENSCH A, HOFFMANN J, et al. Improving language models by retrieving from trillions of tokens[C]//International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2022: 2206-2240. [16] IZACARD G, GRAVE É. Leveraging Passage Retrieval with Generative Models for Open Domain Question Answering[C]//Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Main Volume. 2021: 874-880. [17] KHANDELWAL U, LEVY O, JURAFSKY D, et al. Generalization through Memorization: Nearest Neighbor Language Models[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations. 2019. [18] HE J, NEUBIG G, Berg-Kirkpatrick T. Efficient Nearest Neighbor Language Models[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2021: 5703-5714. [19] HE Z, ZHONG Z, CAI T, et al. REST: Retrieval-Based Speculative Decoding[C]//Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2024: 1582-1595. [20] FU B, FENG D. GPTCache: An Open-Source Semantic Cache for LLM Applications Enabling Faster Answers and Cost Savings[C]//The 3rd Workshop for Natural Language Processing Open Source Software (NLP-OSS). 2023: 212. [21] ZHAO P, ZHANG H, YU Q, et al. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for AI-Generated Content: A Survey[J]. CoRR, 2024. [22] GAO Y, XIONG Y, GAO X, et al. Retrieval-augmented generation for large language models: A survey[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.10997, 2023. [23] FAN W, DING Y, NING L, et al. A survey on rag meeting llms: Towards retrieval-augmented large language models[C]//Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. 2024: 6491-6501. [24] CHEN J, LIN H, HAN X, et al. Benchmarking large language models in retrieval-augmented generation[C]// Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2024, 38(16): 17754-17762. [25] IlIN I. Advanced RAG techniques: an illustrated overview [EB/OL].(2023).https://github.com/NirDiamant/RAG_TECHNIQUES. [26] ZHENG H S, MISHRA S, CHEN X, et al. Take a Step Back: Evoking Reasoning via Abstraction in Large Language Models[C]//The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations. [27] WANG S, XU Y, FANG Y, et al. Training Data is More Valuable than You Think: A Simple and Effective Method by Retrieving from Training Data[C]//Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2022: 3170-3179. [28] MA X, GONG Y, HE P, et al. Query Rewriting in RetrievalAugmented Large Language Models[C]// Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2023: 5303-5315. [29] KHATTAB O, SANTHANAM K, LI X L, et al. Demonstratesearch-predict: Composing retrieval and language models for knowledge-intensive nlp[J]. arxiv preprint arxiv:2212.14024, 2022. [30] WANG Y, LI P, SUN M, et al. Self-Knowledge Guided Retrieval Augmentation for Large Language Models[C]// The 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [31] JEONG S, BAEK J, CHO S, et al. Adaptive-RAG: Learning to Adapt Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models through Question Complexity[C]//Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2024: 7029-7043. [32] SHAO Z, GONG Y, HUANG M, et al. Enhancing Retrieval- Augmented Large Language Models with IterativeRetrieval- Generation Synergy[C]//The 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [33] ZHA L, ZHOU J, LI L, et al. Tablegpt: Towards unifying tables, nature language and commands into one gpt[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2307.08674, 2023. [34] GAUR M, GUNARATNA K, SRINIVASAN V, et al. Iseeq: Information seeking question generation using dynamic meta-information retrieval and knowledge graphs[C]// Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2022, 36(10): 10672-10680. [35] YANG L, CHEN H, LI Z, et al. Give us the facts: Enhancing large language models with knowledge graphs for fact-aware language modeling[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2024. [36] HE X, TIAN Y, SUN Y, et al. G-retriever: Retrieval- augmented generation for textual graph understanding and question answering[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.07630, 2024. [37] TEJA R. Evaluating the ideal chunk size for a rag system using llamaindex[J]. LLAMAi, [Online]. Available: https:// www.llamaindex.ai/blog/evaluating-the-idealchunk-size- for-a-ragsystem-using-llamaindex6207e5d3fec5, 2023, 30: 31. [38] YANG S. “Advanced rag 01: Small-tobig retrieval[EB/OL]. (2023-11-05)[2024-10-01].https://towardsdatascience.com/advanced-rag-01-small-to-big-retrieval172181b396d4. [39] QIAN H, LIU Z, MAO K, et al. Grounding Language Model with Chunking-Free In-Context Retrieval[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.09760, 2024. [40] ZHAO J, JI Z, QI P, et al. Meta-Chunking: Learning Efficient Text Segmentation via Logical Perception[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.12788, 2024. [41] LIANG Y, JIANG Z, YIN D, et al. RAAT: Relation-Augmented Attention Transformer for Relation Modeling in Document-Level Event Extraction[C]//Pro- ceedings of the 2022 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. 2022: 4985-4997. [42] SUN Z, WANG X, TAY Y, et al. Recitation-Augmented Language Models[C]//The Eleventh International Con- ference on Learning Representations. [43] WANG K, REIMERS N, Gurevych I. DAPR: A Benchmark on Document-Aware Passage Retrieval[J]. arxiv preprint arxiv:2305.13915, 2023. [44] KIM J, NAM J, MO S, et al. SuRe: Summarizing Retrievals using Answer Candidates for Open-domain QA of LLMs[C]//The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations. [45] DOOSTMOJAMMADI E, NORLUND T, KUHLMANN M, et al. Surface-Based Retrieval Reduces Perplexity of Retrieval-Augmented Language Models[C]//Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 2: Short Papers). 2023: 521-529. [46] XIAO S, LIU Z, ZHANG P, et al. C-pack: Packed resources for general chinese embeddings[C]//Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. 2024: 641649. [47] LIU Z, XIAO S, SHAO Y, et al. RetroMAE-2: Duplex Masked Auto-Encoder For Pre-Training Retrieval-Oriented Language Models[C]//Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2023: 2635-2648. [48] SHI W, MIN S, YASUNAGA M, et al. REPLUG: RetrievalAugmented Black-Box Language Models[C]// Proceedings of the 2024 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2024: 8364-8377. [49] ZHANG L, YU Y, WANG K, et al. Arl2: Aligning retrievers for black-box large language models via self-guided adaptive relevance labeling[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.13542, 2024. [50] DAI Z, ZHAO V Y, MA J, et al. Promptagator: Few-shot Dense Retrieval From 8 Examples[C]//The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations. [51] LUO K, LIU Z, XIAO S, et al. BGE Landmark Embedding: A Chunking-Free Embedding Method For Retrieval Augmented Long-Context Large Language Models[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.11573, 2024. [52] LI X, LI J. Angle-optimized text embeddings[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.12871, 2023. [53] YOON S, CHOI E, KIM J, et al. ListT5: Listwise Reranking with Fusion-in-Decoder Improves Zero-shot Retrieval[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.15838, 2024. [54] GAO L, MA X, LIN J, et al. Precise Zero-Shot Dense Retrieval without Relevance Labels[C]//Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2023: 1762-1777. [55] SARTHI P, ABDULLAH S, TULI A, et al. RAPTOR: Recursive Abstractive Processing for Tree-Organized Retrieval[C]//The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations. [56] WANG Y, LIPKA N, ROSSI R A, et al. Knowledge graph prompting for multi-document question answering[C]//Pro- ceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2024, 38(17): 19206-19214. [57] RACKAUCKAS Z. RAG-Fusion: a New Take on RetrievalAugmented Generation[J]. International Journal on Natural Language Computing (IJNLC) Vol, 2024, 13. [58] ZHOU D, SVHARLI N, HOU L, et al. Least-to-Most Prompting Enables Complex Reasoning in Large Language Models[C]//The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations. [59] PENG W, LI G, JIANG Y, et al. Large language model based long-tail query rewriting in taobao search[C]// Companion Proceedings of the ACM on Web Conference 2024. 2024: 20-28. [60] LI X, NIE E, LIANG S. From Classification to Generation: Insights into Crosslingual Retrieval Augmented ICL[C]// NeurIPS 2023 Workshop on Instruction Tuning and Instruction Following. [61] KARPUKHIN V, OGUZ B, MIN S, et al. Dense passage retrieval for open-domain question answering[C]//2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, EMNLP 2020. Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2020: 6769-6781. [62] CHENG D, HUANG S, BI J, et al. UPRISE: Universal Prompt Retrieval for Improving Zero-Shot Evaluation[C]// The 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [63] YOON J, CHEN Y, ARIK S, et al. Search-Adaptor: Embedding Customization for Information Retrieval[C]// Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2024: 12230-12247. [64] YANG H, LI Z, ZHANG Y, et al. PRCA: Fitting Black-Box Large Language Models for Retrieval Question Answering via Pluggable Reward-Driven Contextual Adapter[C]//Pro- ceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2023: 5364-5375. [65] YAN S Q, GU J C, ZHU Y, et al. Corrective retrieval augmented generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.15884, 2024. [66] YU W, ITER D, WANG S, et al. Generate rather than Retrieve: Large Language Models are Strong Context Generators[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations. 2023. [67] LUO Z, XU C, ZHAO P, et al. Augmented large language models with parametric knowledge guiding[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.04757, 2023. [68] MA Y, CAO Y, HONG Y C, et al. Large Language Model Is Not a Good Few-shot Information Extractor, but a Good Reranker for Hard Samples![C]//The 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [69] DONGJ, FATEMI B, PEROZZI B, et al. Don’t Forget to Connect! Improving RAG with Graph-based Reranking[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.18414, 2024. [70] YU Y, PING W, LIU Z, et al. RankRAG: Unifying Context Ranking with Retrieval-Augmented Generation in LLMs[C]//The Thirty-eighth Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. [71] ANDERSON N, WILSON C, RICHARDSON S D. Lingua: Addressing scenarios for live interpretation and automatic dubbing[C]//Proceedings of the 15th Biennial Conference of the Association for Machine Translation in the Americas (Volume 2: Users and Providers Track and Government Track). 2022: 202-209. [72] JIANG H, WU Q, LUO X, et al. Longllmlingua: Accelerating and enhancing llms in long context scenarios via prompt compression[J]. arxiv preprint arxiv:2310.06839, 2023. [73] WANG Z, ARAKI J, JIANG Z, et al. Learning to filter context for retrieval-augmented generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.08377, 2023. [74] XU F, SHI W, CHOI E. Recomp: Improving retrieval- augmented lms with compression and selective augmentation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2310.04408, 2023. [75] KIM Y, KIM H J, PARK C, et al. Adaptive Contrastive Decoding in Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Handling Noisy Contexts[J]. CoRR, 2024. [76] ZHU K, FENG X, DU X, et al. An Information Bottleneck Perspective for Effective Noise Filtering on Retrieval- Augmented Generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406. 01549, 2024. [77] CUI J, LI Z, YAN Y, et al. Chatlaw: Open-source legal large language model with integrated external knowledge bases[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.16092, 2023. [78] LI W, LI J, RAMOS R, et al. Understanding Retrieval Robustness for Retrieval-Augmented Image Captioning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.02265, 2024. [79] LI X, LIU Z, XIONG C, et al. Structure-Aware Language Model Pretraining Improves Dense Retrieval on Structured Data[C]//Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2023. 2023: 11560-11574. [80] SHI T, LI L, LIN Z, et al. Dual-Feedback Knowledge Retrieval for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems[C]// Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2023: 6566-6580. [81] LIN X V, CHEN X, CHEN M, et al. RA-DIT: Retrieval-Augmented Dual Instruction Tuning[C]//The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations. [82] ROSSET C, CHUNG H L, QIN G, et al. Researchy Questions: A Dataset of Multi-Perspective, Decomposi- tional Questions for LLM Web Agents[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.17896, 2024. [83] FENG J, TAO C, GENG X, et al. Synergistic Interplay between Search and Large Language Models for Information Retrieval[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.07402, 2023. [84] SHAO Z, GONG Y, HUANG M, et al. Enhancing RetrievalAugmented Large Language Models with IterativeRetrievalGeneration Synergy[C]//The 2023 Conferenceon Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [85] LI M, MIAO S, LI P. Simple is effective: The roles of graphs and large language models in knowledge- graph-based retrieval-augmented generation[J]. arxiv preprint arxiv:2410.20724, 2024. [86] Tan J, Dou Z, Zhu Y, et al. Small Models, Big Insights: Leveraging Slim Proxy Models To Decide When and What to Retrieve for LLMs[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.12052, 2024. [87] YUE Z, ZENG H, SHANG L, et al. Retrieval Augmented Fact Verification by Synthesizing Contrastive Arguments[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.09815, 2024. [88] WANG Z, LIU A, LIN H, et al. RAT: Retrieval Augmented Thoughts Elicit Context-Aware Reasoning in Long-Horizon Generation[J]. CoRR, 2024. [89] TRIVEDI H, BALASUBRAMANIAN N, KHOT T, et al. Interleaving Retrieval with Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Knowledge-Intensive Multi-Step Questions[C]//Pro- ceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2023: 10014-10037. [90] KIM G, KIM S, JEON B, et al. Tree of Clarifications: Answering Ambiguous Questions with Retrieval- Augmented Large Language Models[C]//Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2023: 996-1009. [91] LI X, ZHAO R, CHIA Y K, et al. Chain of knowledge: A framework for grounding large language models with structured knowledge bases[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.13269, 2023, 3. [92] Zhang J. Graph-toolformer: To empower llms with graph reasoning ability via prompt augmented by chatgpt[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.11116, 2023. [93] NAKANO R, HILTON J, BALAJI S, et al. Webgpt: Browser-assisted question-answering with human feedback[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2112.09332, 2021. [94] JIANG Z, XU F F, GAO L, et al. Active Retrieval Augmented Generation[C]//Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. 2023: 7969-7992. [95] ASAI A, WU Z, WANG Y, et al. Self-RAG: Learning to Retrieve, Generate, and Critique through Self- Reflection[C]//The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations. [96] LU H, LIU Z. Improving Retrieval-Augmented Code Comment Generation by Retrieving for Generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.03623, 2024. [97] XIA Y, ZHOU J, SHI Z, et al. Improving Retrieval Augmented Language Model with Self-Reasoning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.19813, 2024. [98] YANG D, RAO J, CHEN K, et al. Im-rag: Multi-round retrieval-augmented generation through learning inner monologues[C]//Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. 2024: 730-740. [99] WANG C, LONG Q, XIAO M, et al. BioRAG: A RAGLLM Framework for Biological Question Reasoning[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.01107, 2024. [100] LIN X, WANG W, LI Y, et al. Data-efficient Fine-tuning for LLM-based Recommendation[C]//Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. 2024: 365374. [101] OVADIA O, BRIEF M, MISHAELi M, et al. Fine-tuning or retrieval? comparing knowledge injection in llms[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.05934, 2023. [102] SOUDANI H, KANOULAS E, HASIBIi F. Fine tuning vs. retrieval augmented generation for less popular knowledge[C]// Proceedings of the 2024 Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval in the Asia Pacific Region. 2024: 12-22. [103] LEE J, CHEN A, DAI Z, et al. Can Long-Context Language Models Subsume Retrieval, RAG, SQL, and More?[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.13121, 2024. [104] JIANG X, QIU R, ZHANG H, et al. TC-RAG: Turing-Complete RAG’s Case study on Medical LLM Systems[J]. CoRR, 2024. [105] BAMETT S, KUMIAWAN S, THUDUMU S, et al. Seven failure points when engineering a retrieval augmented generation system[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM 3rd International Conference on AI Engineering-Software Engineering for AI. 2024: 194-199. [106] ZHAO X, LU J, DENG C, et al. Beyond One-Model- Fits-All: A Survey of Domain Specialization for Large Language Models[J]. arxiv preprint arxiv:2305.18703, 2023. [107] BLAGOJEVI V. Enhancing rag pipelines in haystack: Introducing diversityranker and lostinthemiddleranker[EB/ OL].(2023-08-09)[2024-1007].https://towardsdatascience.com/enhancing-rag-pipelines-in-haystack-45f14e2bc9f5. [108] SINGHAL R, PATWA P, PATWA P, et al. Evidence-backed Fact Checking using RAG and Few-Shot In-Context Learning with LLMs[J]. CoRR, 2024. [109] LEE J S, Hsiang J. Patent claim generation by fine-tuning OpenAI GPT-2[J]. World Patent Information, 2020, 62: 101983. [110] PARK J S, O’BRIEN J, CAI C J, et al. Generative agents: Interactive simulacra of human behavior[C]//Proceedings of the 36th annual acm symposium on user interface software and technology. 2023: 1-22. [111] WU J, ZHU J, QI Y. Medical Graph RAG: Towards Safe Medical Large Language Model via Graph Retrieval- Augmented Generation[J]. CoRR, 2024. [112] DONG Y, MU R, ZHANG Y, et al. Safeguarding Large Language Models: A Survey[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406. 02622, 2024. [113] ROFFO G. Exploring Advanced Large Language Models with LLMsuite[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.12036, 2024. [114] LENG Q, UHLENHUTH K, POLYZOTIS A. Best practices for llm evaluation of rag applications[EB/OL]. (2023- 0912)[2024-10-07].https://www.databricks.com/blog/LLMauto-eval-best-practices-RAG. [115] ES S, JAMES J, ANKE L E, et al. RAGAs: Automated Evaluation of Retrieval Augmented Generation[C]//Pro- ceedings of the 18th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations. 2024: 150-158. [116] LIU Y, HUANG L, LI S, et al. Recall: A benchmark for llms robustness against external counterfactual knowledge[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.08147, 2023. [117] SAAD-FALCON J, KHATTAB O, POTTS C, et al. ARES: An Automated Evaluation Framework for Retrieval- Augmented Generation Systems[C]//Proceedings of the 2024Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (Volume 1: Long Papers). 2024: 338354. [118] TANG Y, YANG Y. Multihop-rag: Benchmarking retrievalaugmented generation for multi-hop queries[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.15391, 2024. [119] LYU Y, LI Z, NIU S, et al. Crud-rag: A comprehensive chinese benchmark for retrieval-augmented generation of large language models[J]. ACM Transactions on Information Systems, 2024. [120] XIONG G, JIN Q, LU Z, et al. Benchmarking retrieval- augmented generation for medicine[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.13178, 2024. [121] WANG S, KHRAMTSOVA E, ZHUANG S, et al. Feb4rag:Evaluating federated search in the context of retrieval augmented generation[C]//Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. 2024: 763-773. [122] XU Z, LI Y, DING R, et al. Let LLMs Take on the Latest Challenges! A Chinese Dynamic Question Answering Benchmark[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.19248, 2024. [123] WANG S, LIU J, SONG S, et al. DomainRAG: A Chinese Benchmark for Evaluating Domain-specific Retrieval- Augmented Generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406. 05654, 2024. [124] YU X, CHENG H, LIU X, et al. ReEval: Automatic Hallucination Evaluation for Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models via Transferable Adversarial Attacks[C]//Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2024. 2024: 1333-1351. [125] HOFSTATTER S, CHEN J, RAMAN K, et al. Fid-light: Efficient and effective retrieval-augmented text generation[C]//Proceedings of the 46th International ACM SIGIRConference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. 2023: 1437-1447. [126] CUCONASU F, TRAPPOLINIi G, SICILIANO F, et al. The power of noise: Redefining retrieval for rag systems[C]// Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. 2024: 719-729. [127] Salemi A, Zamani H. Evaluating retrieval quality in retrieval-augmented generation[C]//Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. 2024: 2395-2400. [128] ZHU K, LUO Y, XU D, et al. RAGEval: Scenario Specific RAG Evaluation Dataset Generation Framework[J]. CoRR, 2024. [129] RU D, QIU L, HU X, et al. RAGChecker: A Fine-grained Framework for Diagnosing Retrieval-Augmented Generation[C]//The Thirty-eight Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track. [130] TU S, WANG Y, YU J, et al. R-eval: A unified toolkit for evaluating domain knowledge of retrieval augmented large language models[C]//Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discoveryand Data Mining. 2024: 5813-5824. [131] WANGA, PRUKSACHATKUN Y, NANGIA N, et al. SuperGLUE: A Stickier Benchmark for General-Purpose Language Understanding Systems[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 32. [132] PETRONI F, PIKTUS A, FAN A, et al. KILT: a Benchmark for Knowledge Intensive Language Tasks[C]//NAACL-HLT. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021: 2523-2544. [133] YANG Z, QI P, ZHANG S, et al. HotpotQA: A Dataset for Diverse, Explainable Multi-hop Question Answering[C]// Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018. [134] THOME J, VLACHOS A, CHRISTODOULOPOULOS C, et al. FEVER: A large-scale dataset for fact extraction and verification[C]//2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, NAACL HLT 2018. Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2018: 809-819. [135] DINAN E, ROLLERr S, SHUSTER K, et al. Wizard of Wikipedia: Knowledge-Powered Conversational Agents[C]// International Conference on Learning Representations. [136] DEYOUNG J, JAIN S, RAJANIi N F, et al. ERASER: A Benchmark to Evaluate Rationalized NLP Models[C]// Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020. [137] Zhang S, Liu X, Liu J, et al. Record: Bridging the gap between human and machine commonsense reading comprehension[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.12885, 2018. [138] GOTTSCHALK S, DEMIDOVA E. Eventkg: A multilingual event-centric temporal knowledge graph[C]//The Semantic Web: 15th International Conference, ESWC 2018, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, June 3–7, 2018, Proceedings 15. Springer International Publishing, 2018: 272-287. [139] HUANG J, SHAO H, CHANG K C C, et al. Understanding Jargon: Combining Extraction and Generation for Definition Modeling[C]//2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, EMNLP 2022. 2022. [140] KWIATKOWSHI T, PALOMAKI J, REDFIELD O, et al. Natural questions: a benchmark for question answering research[J]. Transactions of the Association for Com- putational Linguistics, 2019, 7: 453-466. [141] LIANG X, SONG S, NIU S, et al. Uhgeval: Benchmarking the hallucination of chinese large language models via unconstrained generation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311. 15296, 2023. [142] KAMALLOO E, THAKUR N, LASSANCE C, et al. Resources for brewing BEIR: reproducible reference models and an official leaderboard[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2306.07471, 2023. [143] KASAI J, SAKAGUCHI K, LE B R, et al. REALTIME QA: what’s the answer right now?[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2024, 36. [144] FISCH A, TALMOR A, JIA R, et al. Mrqa 2019 shared task: Evaluating generalization in reading comprehension[C]// 2nd Workshop on Machine Reading for Question Answering, MRQA@ EMNLP 2019. Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), 2019: 1-13. [145] ZHENG L, CHIANG W L, SHENG Y, et al. Judging LLMas-a-judge with MT-bench and Chatbot Arena[C]// Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2023: 46595-46623. [146] GIENAPP L, SCELLS H, DECKERS N, et al. Evaluating generative ad hoc information retrieval[C]//Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval. 2024: 1916- 1929. [147] PAPINENI K, ROUKOS S, WARD T, et al. Bleu: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation[C]//Pro- ceedings of the 40th annual meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. 2002: 311-318. [148] FEI Z, SHEN X, ZHU D, et al. LawBench: Benchmarking Legal Knowledge of Large Language Models[J]. CoRR, 2023. [149] MULUDI K, FITRIA K M, TRILOKA J. Retrieval- Augmented Generation Approach: Document Question Answering using Large Language Model[J]. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science & Applications, 2024, 15(3). [150] KURATOV Y, BULATOV A, ANOKGIN P, et al. In search of needles in a 10m haystack: Recurrent memory finds what llms miss[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.10790, 2024. [151] Edge D, Trinh H, Cheng N, et al. From local to global: A graph rag approach to query-focused summarization[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.16130, 2024. [152] YASUUNAGA M, AGHAJANYAN A, SHI W, et al. Retrieval-Augmented Multimodal Language Modeling[C]// International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2023: 39755-39769. [153] LI J, LI D, SAVARESE S, et al. Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models[C]//International conference on machine learning. PMLR, 2023: 19730-19742. [154] ZHU W, YAN A, LU Y, et al. Visualize Before You Write: Imagination-Guided Open-Ended Text Generation[C]// Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EACL 2023. 2023: 78-92. [155] ZHAO J, HAFFARI G, SJAREGHI E. Generating Synthetic Speech from SpokenVocab for Speech Translation[C]// Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EACL 2023. 2023: 1975-1981. [156] CHAN D M, GHOSH S, RASTROW A, et al. Using external off-policy speech-to-text mappings in contextual end-to-end automated speech recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.02736, 2023. [157] YANG A, NAGRANI A, SEO P H, et al. Vid2seq: Large-scale pretraining of a visual language model for dense video captioning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2023: 1071410726. [158] NASHID N, SINTAHA M, MESBAH A. Retrieval-based prompt selection for code-related few-shot learning[C]// 2023 IEEE/ACM 45th International Con- ference on Software Engineering (ICSE). IEEE, 2023: 2450-2462. [159] DU Y, LI S, TORRALBA A, et al. Improving Factuality and Reasoning in Language Models through Multiagent Debate[C]//Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning. [160] LIANG T, HE Z, JIAO W, et al. Encouraging divergent thinking in large language models through multi-agent debate[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.19118, 2023. [161] ChEN J C Y, SAHA S, BANSALl M. Reconcile: Roundtable conference improves reasoning via consensus among diverse llms[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.13007, 2023. [162] WEI J, WANG X, SCHUURMANS D, et al. Chain-ofthought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2022, 35: 24824-24837.
